Introduction
Even if we don't realize it, camera systems in today's world are a vital tool for our public safety. Industries such as automotive and security rely heavily on cameras and sensors to ensure that public safety standards are met and exceeded. These systems are continuously under development to improve their overall effectiveness once they leave the test lab. Thus, introducing infrared capabilities was a logical step in the progression of these types of systems.
At Image Engineering, we have created a NIR* (near-infrared) product line of illumination devices and test charts to help you accurately reproduce NIR light for camera performance evaluation in near-infrared scenarios.
Practical use of infrared sensors
Infrared technology has a meaningful impact on cameras and sensors across various industries. In particular, ADAS and other automotive systems are benefiting from utilizing infrared in their designs. For an ADAS system, cameras and sensors must detect and analyze all of the data in their field of view to make the necessary adjustments. Naturally, object detection must be possible even when operating in darkness or other low visibility weather conditions.
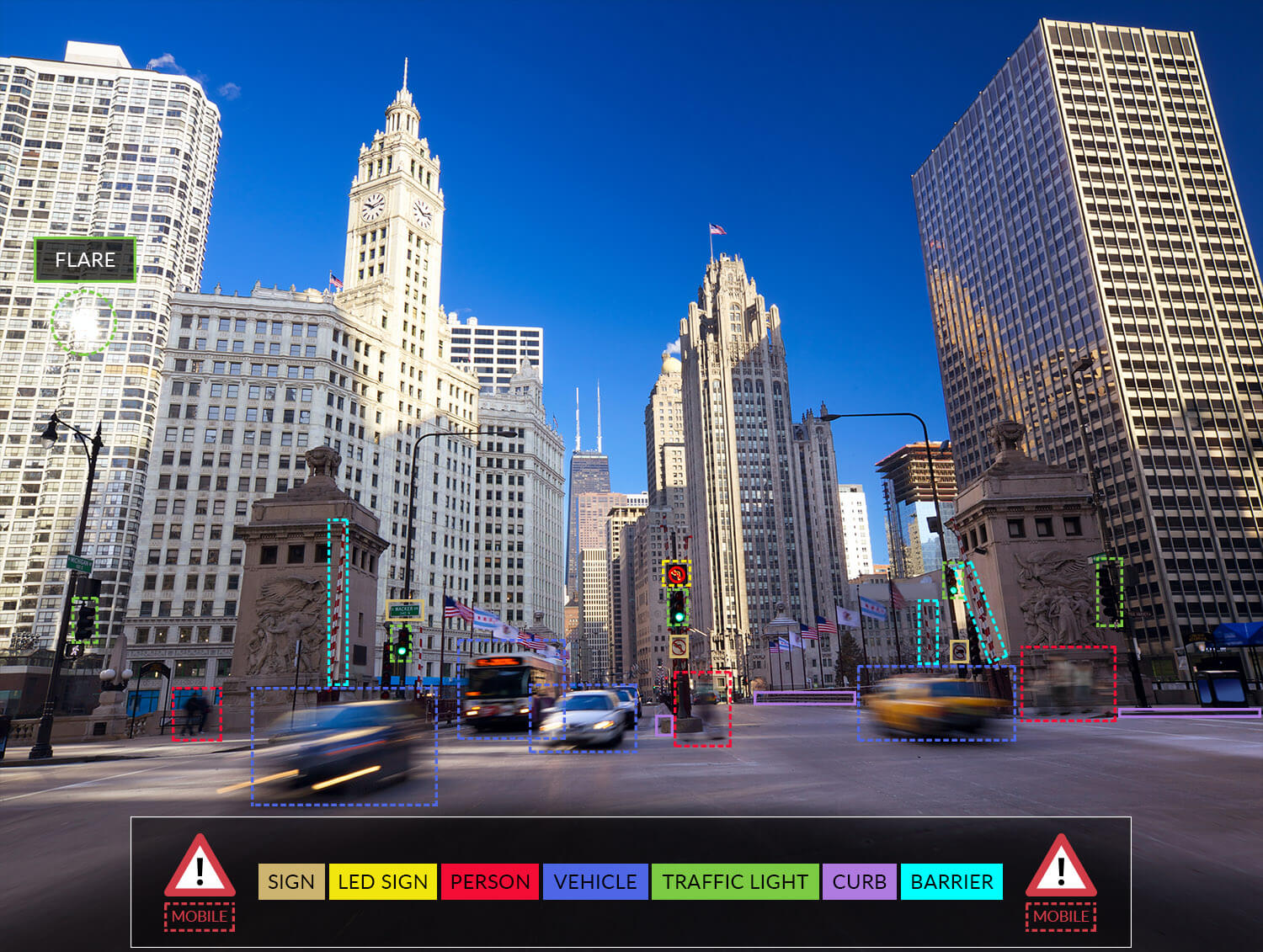

The key benefit of NIR is the ability of the camera to operate in a light mode that a human observer cannot see. In other words, you can have active illumination without the observer being able to see the lighting. For example, when you are driving, your face and those around you can be illuminated with 940 nm light without us realizing it. A different example is when a mobile phone uses FaceID. Essentially, the phone will send out light at 940 nm to illuminate your face for recognition.
An ADAS comprises various systems, including LIDAR, radar, and different visual systems. Integrating infrared cameras into the overall design is crucial to ensuring that the most challenging driving situations can be adequately analyzed, and the safety standards are met before adjusting the vehicle.
NIR system KPIs
Infrared systems are similar to all other camera and sensor systems in that they must be rigorously tested in the lab to ensure they meet standard KPI requirements. As these are unique cameras and infrared light is not visible to the human eye, they require specialized equipment for higher quality testing. Typical KPIs that should be tested in an infrared camera include dynamic range, noise, resolution, texture loss, distortion, and shading.
Choosing the right light source
IR camera testing is like most other forms of camera performance testing. Once you have designated lab space, you must choose the right light source to replicate NIR light conditions. NIR light sources are often difficult to find in the market as they require extensive development for accurate reproduction of NIR light. Most of our light sources use iQ-LED technology for generating custom spectra. We channel this technology through iQ-LED modules with 41 high-power SMD LEDs separated into 20 channels. We create these modules with an additional 11 channels for a wider spectral range for near-infrared measurements.
VIS-IR light sources that we offer
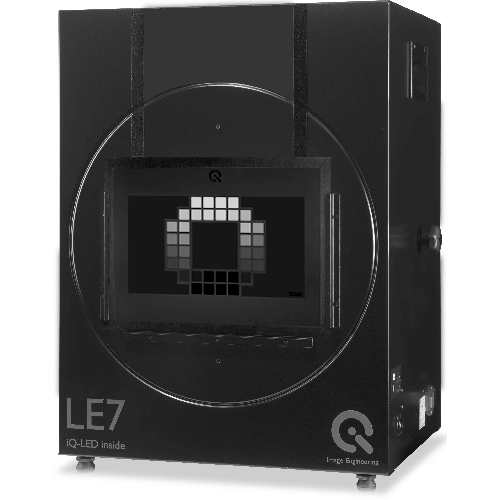

LE7 VIS-IR*
The LE7 is our uniform lightbox that uses iQ-LED technology for transparent chart illumination. The standard LE7 has a spectral range of 350 – 860 nm. The LE7 VIS-IR version uses two iQ-LED VIS-IR (in addition to four standard modules) and extends the spectral range from 380 – 1050 nm for near-infrared measurements.
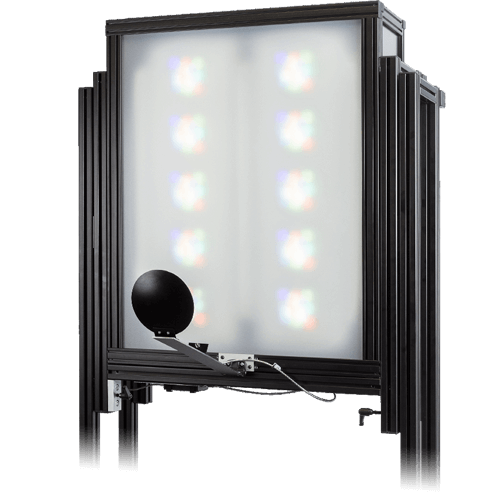

iQ-Flatlight VIS-IR
For reflective chart illumination, we offer the iQ-Flatlights. Each light uses ten iQ-LED modules to create custom spectra. On request, we can build these lights with a combination of the standard iQ-LED and IR modules.
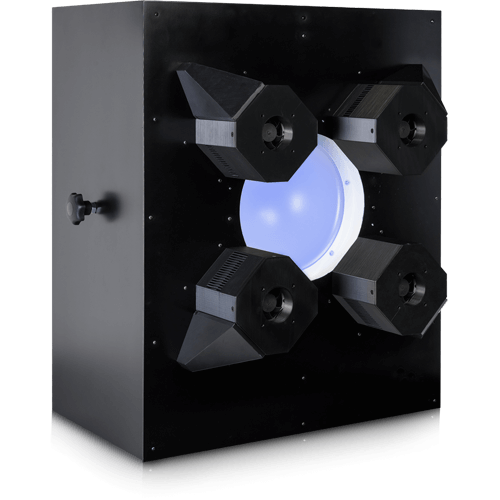

CAL product line
Our CAL product line can also be customized with IR modules. However, unlike the LE7 or iQ-Flatlight, these devices can only be built with standard or IR modules, not both.
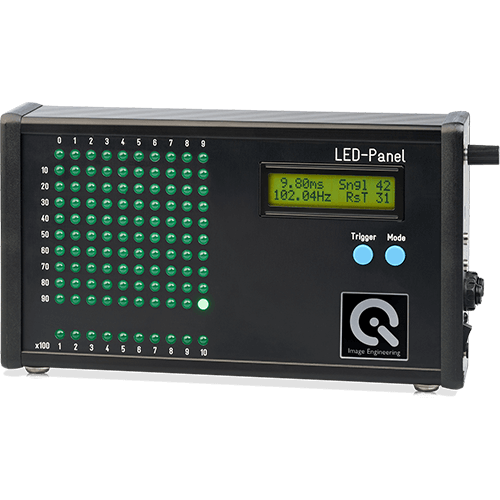

LED-Panel VIS-IR
The LED-Panel is our timing measurement device. We offer two versions of the LED-Panel in the NIR range. The first with a peak wavelength of 850 nm (NIR) and a viewing angle of 80°, the second with a peak wavelength of 940 nm (NIR) and a viewing angle of 90°.
Choosing the correct test chart for NIR testing
Most of our transmissive test charts and many of our reflective (H) test charts can be crafted for NIR testing. Choosing the correct chart depends on the KPI you wish to test.

TE292 VIS-IR
A transparent chart for spectral sensitivity measurements and camera color calibrations
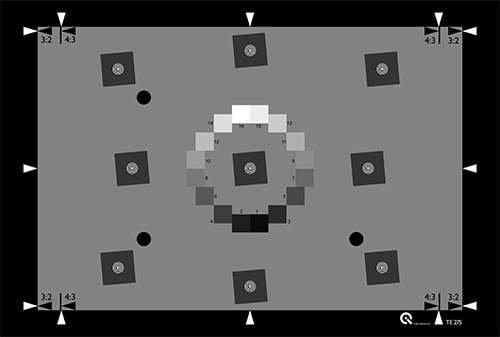
TE275
A slanted edge reflective chart for resolution measurements

TE269
A transparent OECF chart for measuring dynamic range and noise

TE255
A diffuser plate for measuring shading
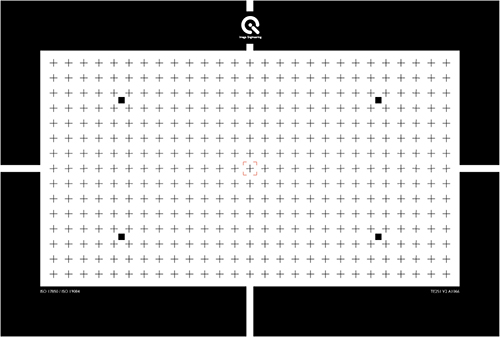
TE251
A reflective or transparent cross chart for distortion measurements

TE42
A multipurpose reflective test chart for measuring various KPIs at once (a few targets, e.g., the color patches and dead leaves cannot be measured using NIR light)
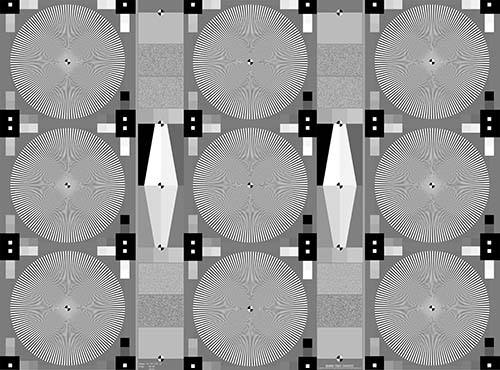
TE253 9x
A transparent or reflective Siemens star chart for resolution and texture loss measurements
See our chart pages for a full list of NIR charts
With the right light source and test chart, you can significantly improve your NIR testing and ultimately create safer and more effective IR camera and sensor systems across all camera industries.
To learn more about NIR testing, don't hesitate to contact our support team at .
For sales inquiries and custom product requests, please contact our sales team at .
*Our light sources cannot produce full infrared because nothing could be seen for the analysis. Instead, we have designed our products to create near-infrared (NIR) illumination for more effective evaluations.
**VIS-IR refers to products that can support standard iQ-LED modules (VIS) and NIR modules (IR) in the same device.

